This week, our focus shifted from theory to implementation as we began shaping our first agentic refactoring prototype.
1. Visualising the Workflow
Last Updated: 25 July
After exploring multi-agent architectures and SkillsBuild certifications, we started formalising how our AI-powered refactoring system should operate end-to-end.
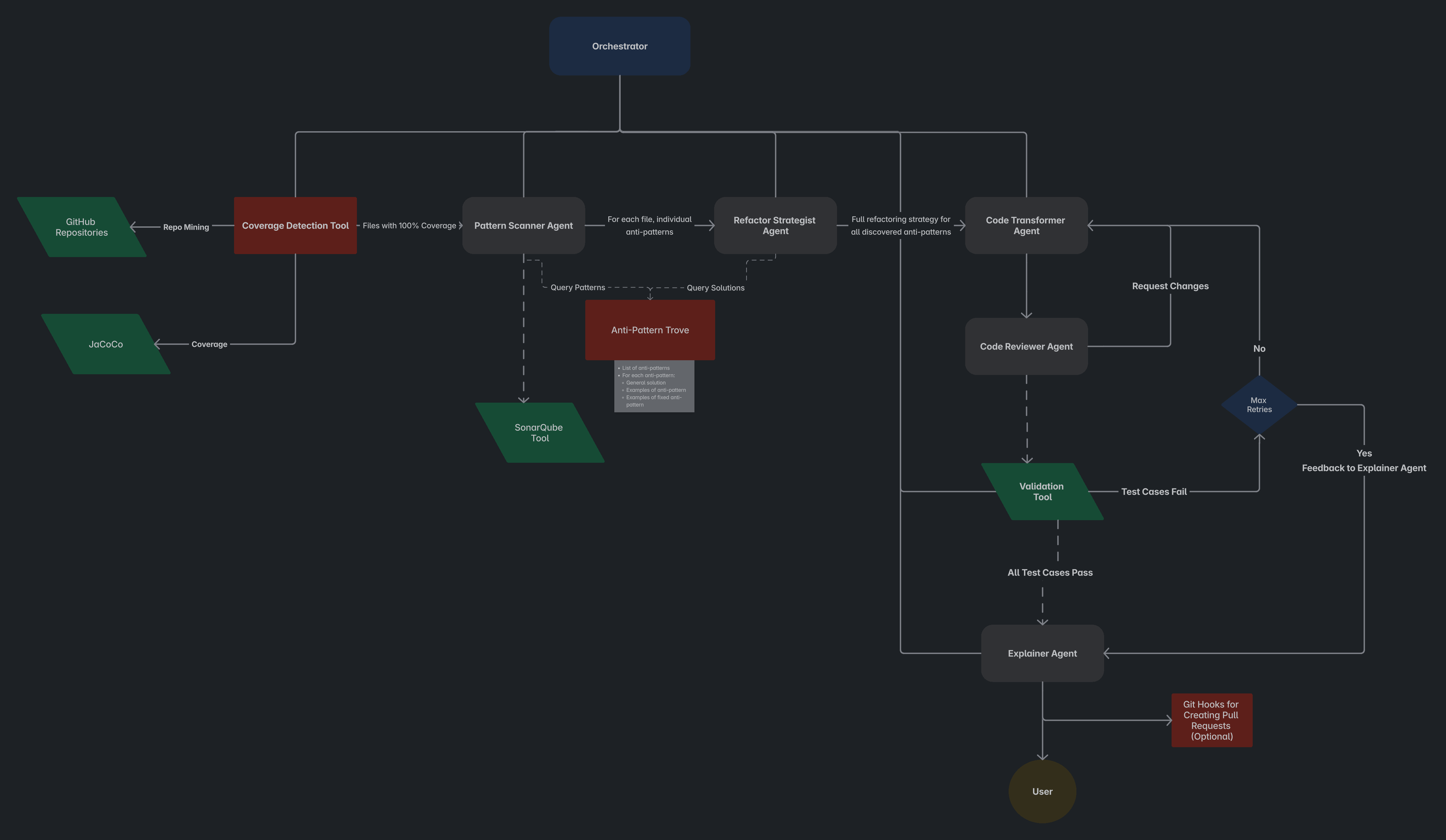
Thanks to Vamsi, who drafted the base structure, we’ve now consolidated our ideas into a clear, modular agentic workflow (click on image to enlarge):
This visual helps guide our implementation roadmap, defining how agents interact, what tools they invoke, and how decisions flow through the system.
Agents
- Pattern Scanner - Is provided a Java file and uses RAG with the help of our Anti-Pattern Trove and (optionally) static analysis tools to find any and all instances of anti-patterns in the provided code. It then compiles a list of these anti-patterns and where they are located.
- Refactor Strategist - Given the aforementioned list, it uses the knowledge from the Anti-Pattern Trove to define a comprehensive strategy to fix all anti-patterns, taking into account the cumulative impact of all changes.
- Code Transformer - Applies the generated strategy by creating a new Java file with the necessary changes to remove the anti-patterns.
- Code Reviewer - Reviews the transformed code and (potentially) requests changes, entering a loop with the Transformer.
- Explainer - Uses the information from the Strategist and Transformer to create a human-readable explanation of the anti-patterns discovered, why they are problematic, and the steps taken to solve them. Optionally, this information will be used to create commit and/or pull request messages for automatic code updates.
- Orchestrator - Orchestrates the other agents (and tools) and ensures a proper control flow.
Tools
- Anti-Pattern Trove - A vector database that contains a custom-built list of anti-patterns, with:
- Explanations - What is the anti-pattern?
- Problems - Why is the anti-pattern problematic?
- Possible Fixes - How to fix/remove the anti-pattern?
- Limitations - When do the fixes not work or should be skipped?
- Examples - What do these patterns look like in real projects (open-source examples)?
- Coverage Detection Tool - A small scripting tool to retrieve coverage from a given repository (e.g., through JaCoCo).
- Custom Components for Static Analysis - Scripting tools to perform static analysis on repositories to provide extra data for the Pattern Scanner agent.
- Git Hooks - Automatic pull request generation.
2. From LangFlow to LangGraph
Our initial prototype was built in LangFlow, a great codeless tool for quick iteration. However, as we moved into versioned collaboration and modular agent behaviours, we migrated to LangGraph for a more code-centric, testable setup.
LangGraph allows us to explicitly define agent transitions, tool dependencies, and recovery behaviour, all critical for refactoring code with high reliability.
Special thanks to Maoqin for setting up the first working version of our agentic pipeline in LangFlow, then LangGraph!
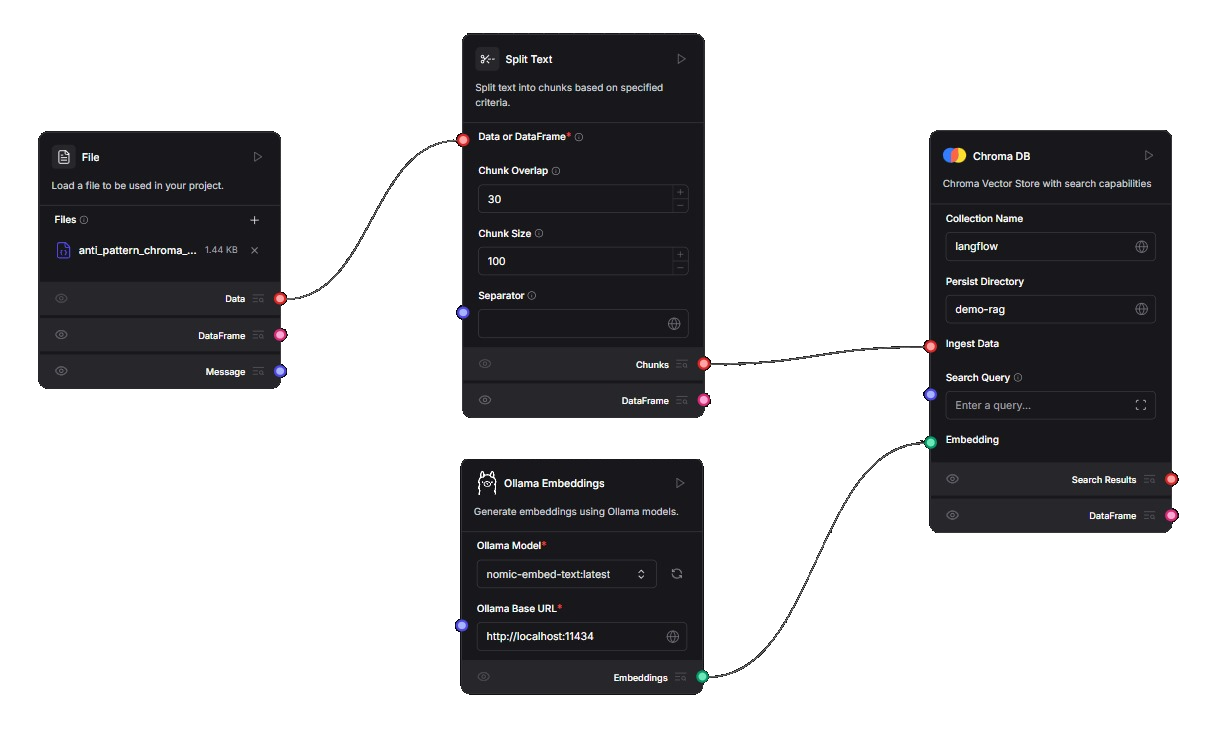
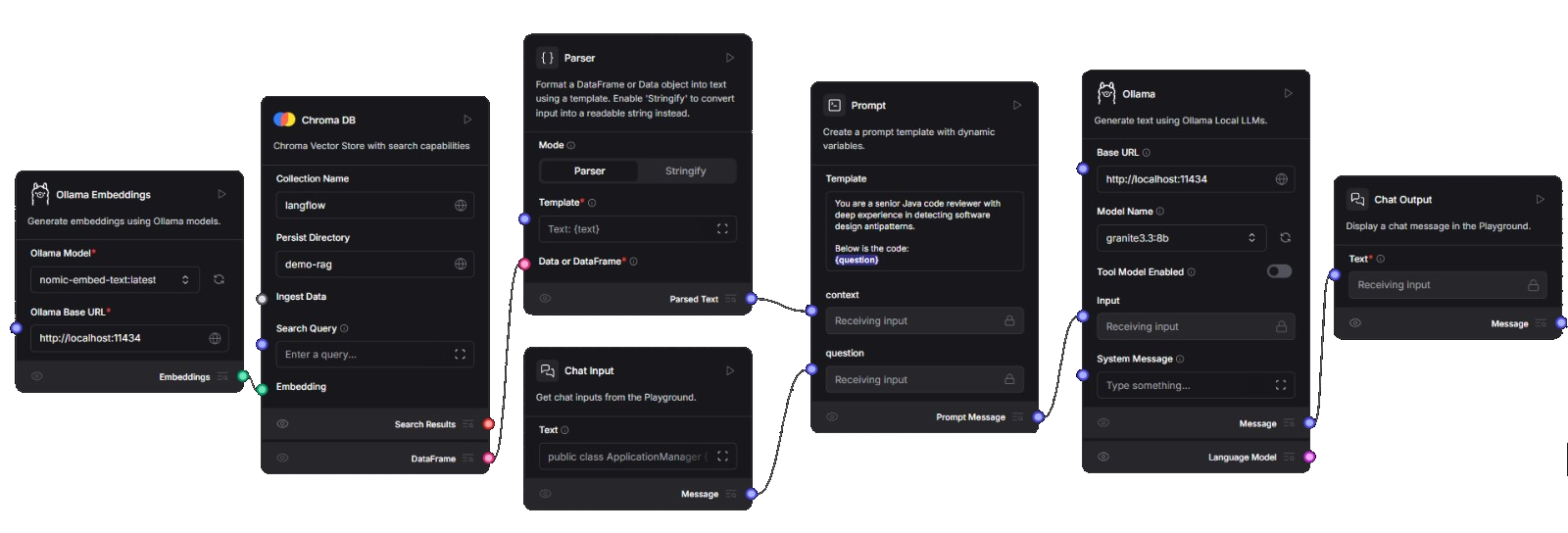
Here is the original LangFlow workflow:
Data Loading Flow
This is an anti-pattern proto-Trove.
Pattern Retriever Flow
This is a pre-agentic version of the Pattern Scanner.
TL;DR
- We designed a modular agentic workflow to guide our AI-powered refactoring system.
- We migrated from LangFlow to LangGraph for greater flexibility and collaboration.
- We’ve begun implementing our first working prototype, thanks to the groundwork laid by Vamsi and Maoqin.